×
☰
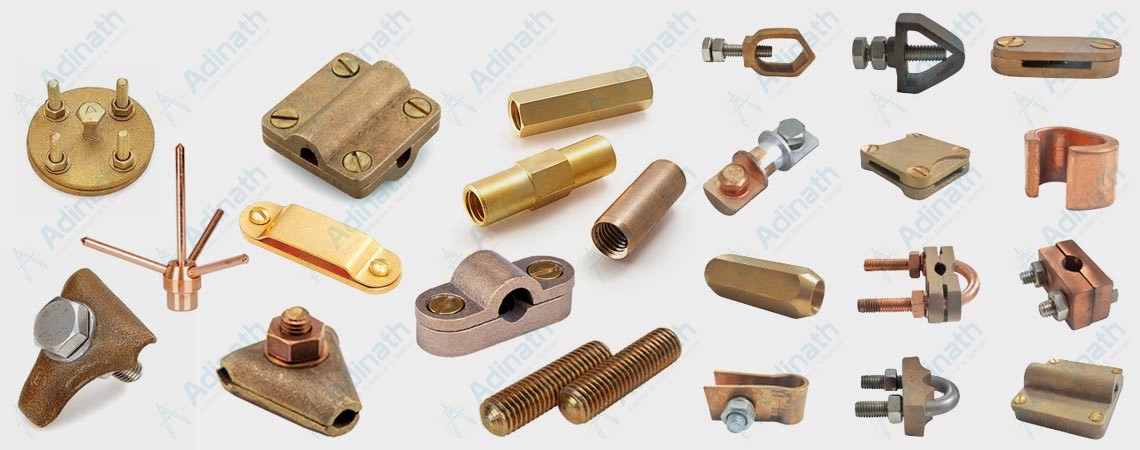
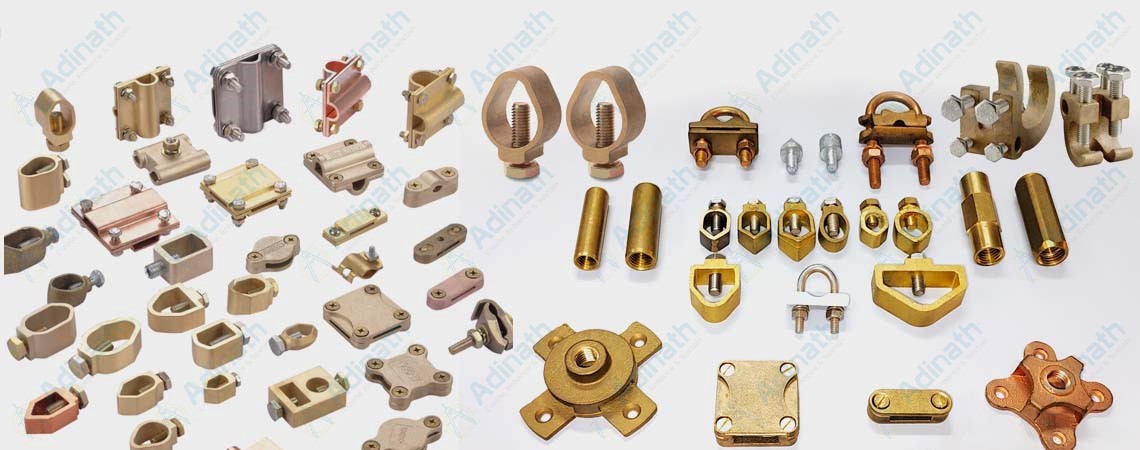
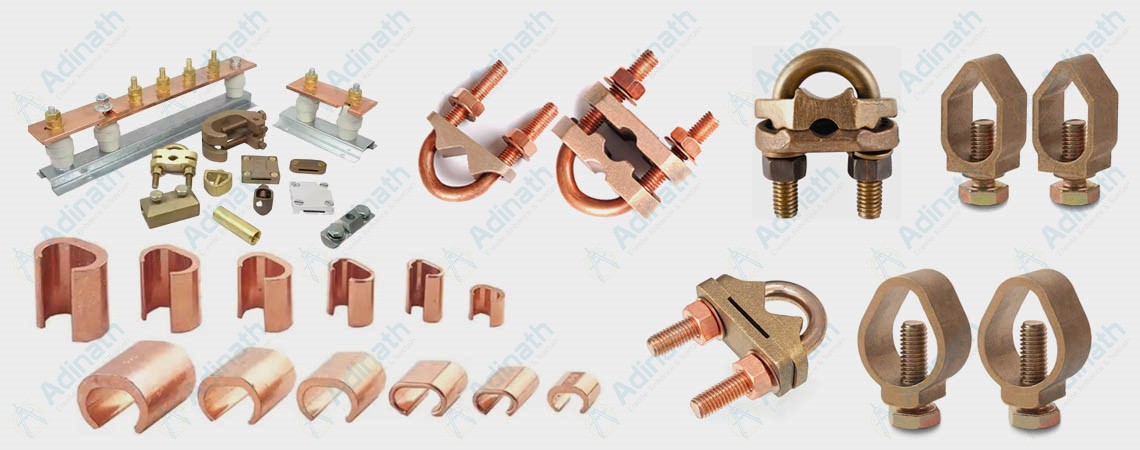
Nickel Aluminium Bronze
Manganese Brronze HighTensile Brass
Tin Bronze
Silicon Bronze
Leaded Tin Bronze
Brass Ingots
Aluminium Bronze Ingots
Silicon Brass
Phosphor Bronze
Gum Metal / Red Brass / Bronze
Quality
Our journey
Infrastructure
Core Purpose & Values
Human Assets / Resource
Management
Capabilities
Environment & CSR
Media Center
Contact Us